Actions & Triggers in Component.json
Actions & Triggers Object
The actions & triggers objects in the component.json describe the actions & triggers that exist within the component.
Actions are operations exposed to the flow builder that can be placed in any step except the first step of a flow.
Triggers are operations exposed to the flow builder that can only be placed in the first step of a flow.
Both action and trigger objects in component.json have similar structures however there are small differences between them which are described in this article.
Each key-value pair in the object represents an action or trigger that is exposed. The string key acts as the identifier for the action/trigger.
The structure used to describe each action or trigger is described below.
If the component has no actions, then the component.json file should not have an actions field. If the component has no triggers, then the component.json file should not have a triggers field. All components must implement at least one action or at least one trigger.
| Property Name | Action/Trigger | Description |
|---|---|---|
| title | Both | Action or trigger’s title to be displayed in the UI |
| description | Both | Action or trigger’s description to be displayed in the UI |
| deprecated | Both | Used to flag the action/trigger as deprecated |
| main | Both | Identifies the code entry point for the action/trigger |
| type | Triggers Only | Identifies if the trigger should be a polling or webhook trigger |
| fields | Both | Identifies config fields which provide flow-level configuration for the action/trigger |
| dynamicMetadata | Both | Signals that the component will dynamically communicate the expected structure of incoming and outgoing messages of the action/trigger |
| metadata | Both | Statically defines the expected structure of incoming and outgoing messages of the action/trigger |
Title & Description
The title and description of the action/trigger to be displayed in the UI
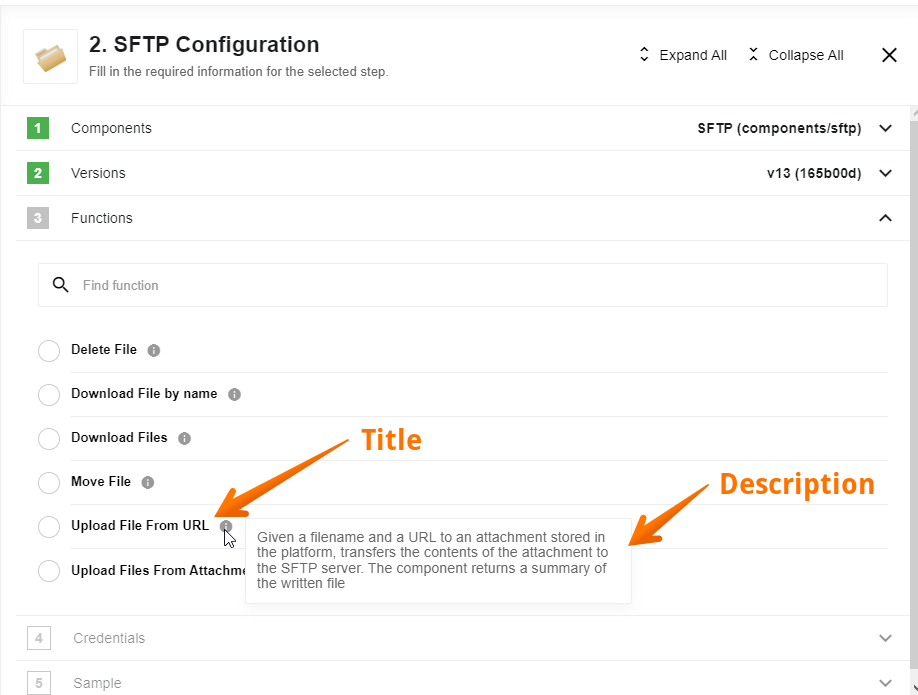
Type: string
Examples:
title:Upsert Objectdescription:Given criteria that matches at most one object, update that object or create it if it does not exist
Deprecated Components and component’s triggers/actions
- An exclamation mark in an orange circle on the flow card indicates that the flow is using a deprecated component or a deprecated trigger/action.
- If you see an exclamation mark in an orange circle next to a component on the flow graph, it means that this component is using a deprecated trigger/action.
- If a component’s icon on the flow graph is shown in gray colour, it means the component itself is deprecated and can no longer be used in new integration flows.
When a component or its functions are marked as deprecated, our team discontinues code maintenance for that specific feature.
Please be aware that we cannot guarantee the continued correct operation of deprecated functions in future component updates. We highly recommend that you migrate away from any deprecated features to ensure seamless functionality and continued support.
We strongly recommend reviewing your integrations and switching to the latest component versions with active functions.
Type: boolean
Default Value: false
Main
Identifies the code entry point for the action/trigger.
In the case of JavaScript components, the code entry point is identified as a path to a .js file which contains the code for the action/trigger. This path should be relative to the root of the component.
In the case of Java components, the code entry point is identified as a fully qualified Java class name which implements the logic for the action/trigger.
Type: string
Examples:
- JavaScript:
./lib/actions/upsertFile.js - Java:
io.elastic.soap.actions.CallAction
Type
Triggers Only
Identifies the type of trigger. There are two options: polling and webhook.
- Setting the value to
pollingwill cause the platform to start the flow at regularly scheduled intervals based on a CRON expression. - Setting the value to
webhookwill cause the platform to generate a URL when the flow is published. The flow will be run when HTTP(S) requests arrive at this URL.
Type: string enum of polling or webhook
Example: polling
Default Value: webhook
Fields Object
The fields object describes the flow specific config fields that need to be configured for the action/trigger.
To learn more about the required structure for this object, see the dedicated article on the fields object for more information.
Metadata: metadata & dynamicMetadata fields
More information on the metadata schema structure can be found in this article.
These two properties indicate how the component will communicate to the platform the expected structure of incoming and outgoing messages.
There are three options for how the message structure is communicated:
- Incoming messages should be mapped to a static structure. The structure of the incoming and outgoing messages are stored in the component repository along with the code.
- Incoming messages should be mapped to a dynamic structure. Once the platform has the credential and config field information, the platform will call a code entry point in the component to learn the metadata.
- Incoming messages should not be mapped.
Dynamic Metadata
If the action/trigger uses dynamic metadata, then
- the
dynamicMetadatavalue should be set - the
metadataproperty should be omitted
Some examples when dynamic metadata is used include:
- There is an action that is modifying an object whose structure can be customized. (E.g. Salesforce allows users to add new object types and tweak the properties/fields stored on existing objects.)
- The required fields change based on the config fields. (E.g. Looking up a page of objects requires different inputs to looking up all objects.)
When dynamic metadata is used, once all required configuration fields for an action/trigger have been submitted, then the platform will call component code to learn the metadata.
- JavaScript: When using dynamic metadata with JavaScript components, the
dynamicMetadatafield should be set to booleantrue. The file containing the action/trigger with dynamic metadata needs to export a functiongetMetaModel()which accepts the credential & config field information and then returns the metadata as an object with two keysinandoutwhich describe the expected structure of incoming and outgoing messages. - Java: When using dynamic metadata with Java components, the
dynamicMetadatafield should be set to a string that is the fully qualified name of a Java class which inherits theio.elastic.api.DynamicMetadataProviderclass.
Whenever a config field is edited, the metadata will be refreshed.
Static Metadata
If the action/trigger uses static metadata, then
- the
dynamicMetadatavalue should be omitted - the
metadataproperty should be set and at least theinproperty should be set.
Some examples when static metadata is used include:
- There is an action that is modifying an object whose structure can never be customized. (E.g. Updating Credit Card Data.)
There are two possible formats for static metadata:
- Metadata is inline in the
component.jsonfile. In this case,metadatais an object with two propertiesinandout. Each property is an object that describes the expected structure of the incoming or outgoing messages. - Metadata is stored in external JSON files. In this case,
metadatais an object with two propertiesinandout. Each property is a string which contains a path (relative to the component’s root directory) to a JSON file which contains an object that describes the expected structure of the incoming or outgoing messages.
No In Metadata
If the action does not expect incoming messages to be transformed by the platform’s built in mapper, then
- the
dynamicMetadatavalue should be omitted - the
metadataproperty should not have a value for theinproperty or be omitted completely
Some examples when no in metadata is used include:
- The action contains mapping logic hardcoded (e.g. code component)
- The action applies JSONata or similar transformations itself (e.g. splitter component)
- The action has no inputs (e.g. configuration component)
When No In Metadata mode is selected, then there will not be a mapping step between this component and the previous component.
Example
(Example of action object implementation in the component.json)
{
"queryAction": {
"title": "Query",
"main": "./lib/actions/query.js",
"metadata": {
"in": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"query": {
"maxLength": "20000",
"title": "SOQL Query",
"type": "string",
"required": "true"
}
}
},
"out": {}
}
}
}